First there is the basic window type simple which consists of just one pane. You can use it to display an arbitrary number of spectra.
There is one special window of window type simple, the plot window.
Since the default frame width for the left and right side is not large
enough to see the scale's inscriptions on your plot you can enlarge
them (see section 4.6 p. ![]() ) or
create a new window named plot which is suitable for the
plotting of spectra.
) or
create a new window named plot which is suitable for the
plotting of spectra.
tv window create simple plot
Besides the simple window there are three different paned
windows, the xy-, x- and y-paned. They are composed of one or more
panes, which are arranged one above the other. All panes share a
common status line. These window types provide a y-scale per pane and
a total of two x-scales. In an xy-paned window the x-scales are
independent as well as the y-scales. The scale at the top of the
window belongs to the uppermost spectrum shown and the one at the
bottom to the lowest. So with more than two panes, you have spectra
without x-scale. In x- or y-paned windows, the x-scales are
coupled to all spectra shown. So if you set x-view markers with
Spacebar in one pane and expand with e, the viewport in
all panes will be changed. In a y-paned window (see figure
4.2 p. ![]() ) all y-scales are
coupled, too.
) all y-scales are
coupled, too.
tv window create {paned xpaned ypaned} name number
Paned windows are good means for the comparison of many spectra. For example you can create an x-paned window for the comparison of four distances of a lifetime experiment with the command:
tv window create xpaned lifetime 4
The remaining window types are composed of two graphic subwindows. The
fit window is an x-paned window in which lower pane the
residuum of the fit is shown. The cut window has a small
subwindow in its upper right corner where the position of the cut
marker in the projection is shown (see figure 2.5
p. ![]() ).
).
tv window create {fit cut} name
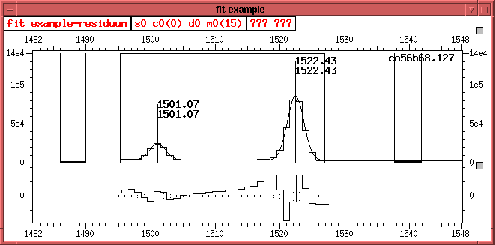
Figure 4.1 on page
![]() shows an example for the fit window
that was created with the command:
shows an example for the fit window
that was created with the command:
tv window create fit ``fit example''
In the lower pane the residuum is displayed.
 |
To delete the graphic window named ``fit example'' use the command:
tv window delete ``fit example''